As team, we went to the field to collect data on how cassava farmers and agricultural experts do cassava disease diagnosis. We figured that most,if not all farmers use their naked eyes to come to a conclusion on which disease the cassava crop is being affected with while the agricultural experts do take leaf or tuber samples to the laboratory so as to carry out disease diagnosis.
We then decided to come up with an alternative i.e. the Mwogonet android mobile application that will be able to localize and classify common diseases in cassava crops such Cassava Mosaic Disease, Cassava Brown Streak Virus and Cassava Bacterial Blight based on the visual signs portrayed on the cassava leaves.
First, we manually annotated cassava leaf images using the Gimp program so as to achieve cropped images.Semantic segmentation was used to classify an image at pixel level with an aim to remove background noise.We achieved this by implementing E-Net - A lightweight model capable of real time semantic segmentation.This gave us an option of training on both cropped and uncropped images to see how well the model learns for those images for the different diseases.
Then,we used the pre-trained VGG16 Convolutional Neural Network(This model is trained on a subset of the ImageNet database which is used in the ImageNet Large-Scale Visual Recognition Challenge (ILSVRC).
The reasons as to why we used VGG16 include;
-
It can be trained on a large dataset therefore makes the model learn more.
-
The model has learned rich feature representations for a wide range of images.
-
Accuracy.The VGG16 model has blocks with same filter size applied multiple times to extract more complex and representative features making it more accurate.
The model was trained on both the cropped and uncropped images for the diseased(Cassava Mosaic Disease, Cassava Bacterial Blight, Cassava Brown Streak Disease and Cassava Green mite Disease) as shown in the table below and we got different weights which reflect how well the model learned i.e.
Below is a summary on the validation accuracy.
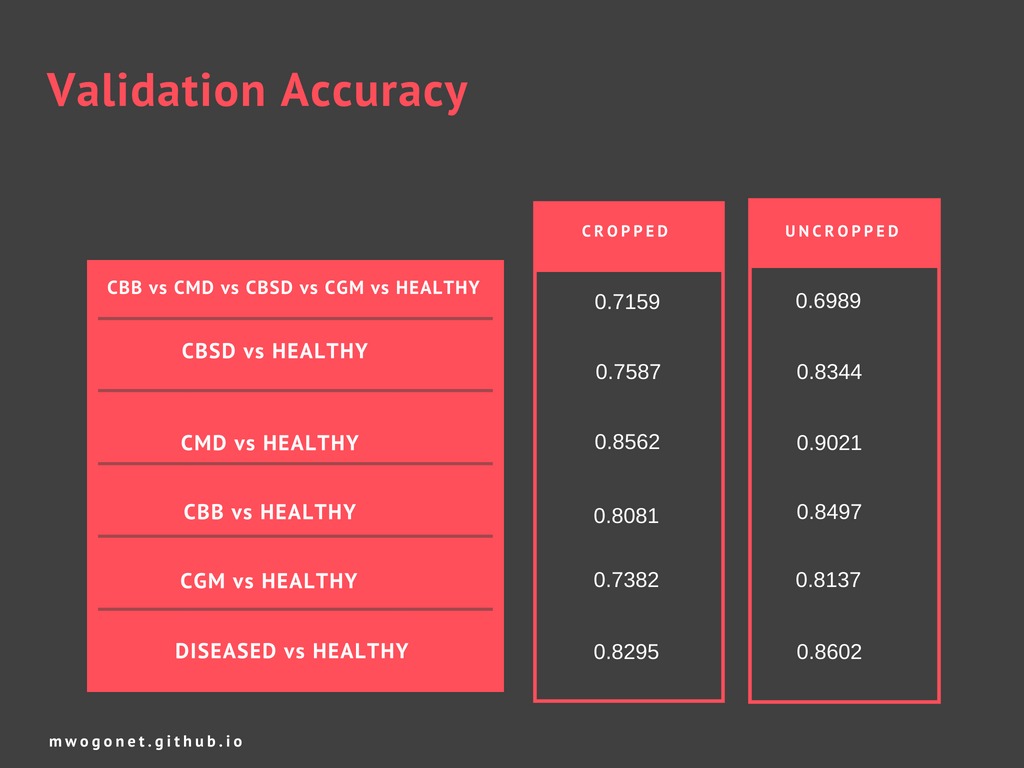
The above weights are then saved as an Hierachical Data Format (HDF) of which we saved ours using version 5 i.e.”Final_weights_0.89.hdf5”.After getting the weights in the form of HDF5, we were required to deploy it on android and this could only be done by converting the h5 graph to a protocol Buffer(PB) file because running the model on android Tensorflow can be done using the “.pb” extension only.The graph is then frozen as a .pb and can be able run on android.
Finally,We deployed our model on an android device. We strategically made use of the Tensorflow Android API and this provided a suitable interface for inference of the machine learning model we had designed. Kotlin programming and Java programming languages were then used in android studio to come up with the android interface and functionality. A simple report and manual are provided on the application to help farmers and agricultural experts use the MwogoNet application easily.Key emphasis was given on the application’s ability to work offline without compromising speed and accuracy of the model.